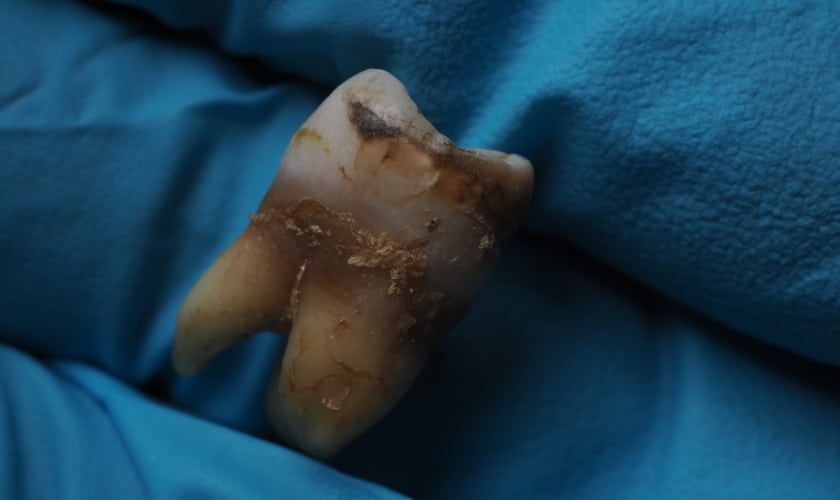
Seeing a black spot on your pearly whites can be a cause for concern. While a bright, white smile is often associated with good health, there are several reasons why teeth can turn black. Let’s delve into the top culprits behind this not-so-desirable transformation.
External Stains: The Usual Suspects
Sometimes, the answer lies in what you put into your body. Certain beverages and foods are notorious for staining teeth. Coffee, tea, red wine, and dark sodas all contain chromogens, pigments that can stick to the enamel, the hard outer layer of your teeth. Over time, these chromogens can build up, leaving behind a dark or discolored appearance. Smoking and tobacco use can also stain teeth, causing a blackening effect.
Enamel Erosion: When Your Shield Weakens
Enamel is tough, but it’s not invincible. Acidic foods and drinks like citrus fruits, soda, and sports drinks can erode enamel over time. This erosion thins the enamel, making the dentin layer beneath it more visible. Dentin is naturally yellow, and when it shows through, it can contribute to a darker tooth appearance. Additionally, eroded enamel is more susceptible to staining from chromogens.
Cavities: The Trouble Beneath the Surface
Cavities, also known as dental caries, are another reason teeth can turn black. These holes form when bacteria in your mouth feed on sugar and produce acid. The acid eats away at the tooth enamel, creating cavities. As the cavity grows deeper, it can reach the dentin layer, causing a blackening effect. If left untreated, cavities can progress to the pulp, the inner part of the tooth, which can also cause the tooth to darken significantly.
Trauma and Internal Bleeding: When Accidents Happen
A blow to the mouth can damage the blood vessels and nerves inside the tooth. This internal bleeding can discolor the tooth, causing it to turn black or gray. In some cases, the tooth may die completely, leading to a darker shade.
Certain Medications: Sometimes the Cure Has Side Effects
Some medications, such as certain antibiotics taken during childhood, can stain teeth as they develop. Iron supplements can also leave behind a dark discoloration. If you’re concerned about medication-related staining, talk to your doctor or dentist.
What to Do About Black Teeth
If you notice blackening on your teeth, the first step is to schedule an appointment with dentist. They can examine your teeth and determine the cause of the discoloration. Here are some possible treatment options:
- Professional Cleaning: For external stains, a professional cleaning by your dentist can remove the buildup and restore your teeth’s natural color.
- Teeth Whitening: If the staining is more extensive or affects deeper layers of the tooth, teeth whitening treatments may be recommended. Your dentist can discuss different whitening options to achieve your desired results.
- Fillings or Crowns: For cavities or damaged teeth, fillings or crowns may be necessary to restore the tooth structure and improve its appearance.
- Root Canal: In severe cases, where the pulp of the tooth is infected or dead, a root canal treatment may be needed to save the tooth.
Prevention is Key
The best way to deal with black teeth is to prevent them in the first place. Here are some tips:
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day for two minutes each time, and floss daily to remove plaque and bacteria.
- Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks: Rinsing your mouth with water after consuming these can help reduce staining.
- Don’t smoke or use tobacco products.
- See your dentist regularly: Regular checkups and cleanings can help identify and address problems early on.
By following these tips and maintaining good oral hygiene, you can keep your smile bright and healthy for years to come. Remember, if you notice any changes in your teeth, don’t hesitate to reach out to your dentist for professional advice.